In my last article, I made a mention about car accidents being the second leading cause of head injuries in America, making up more than 17% of all head injuries.
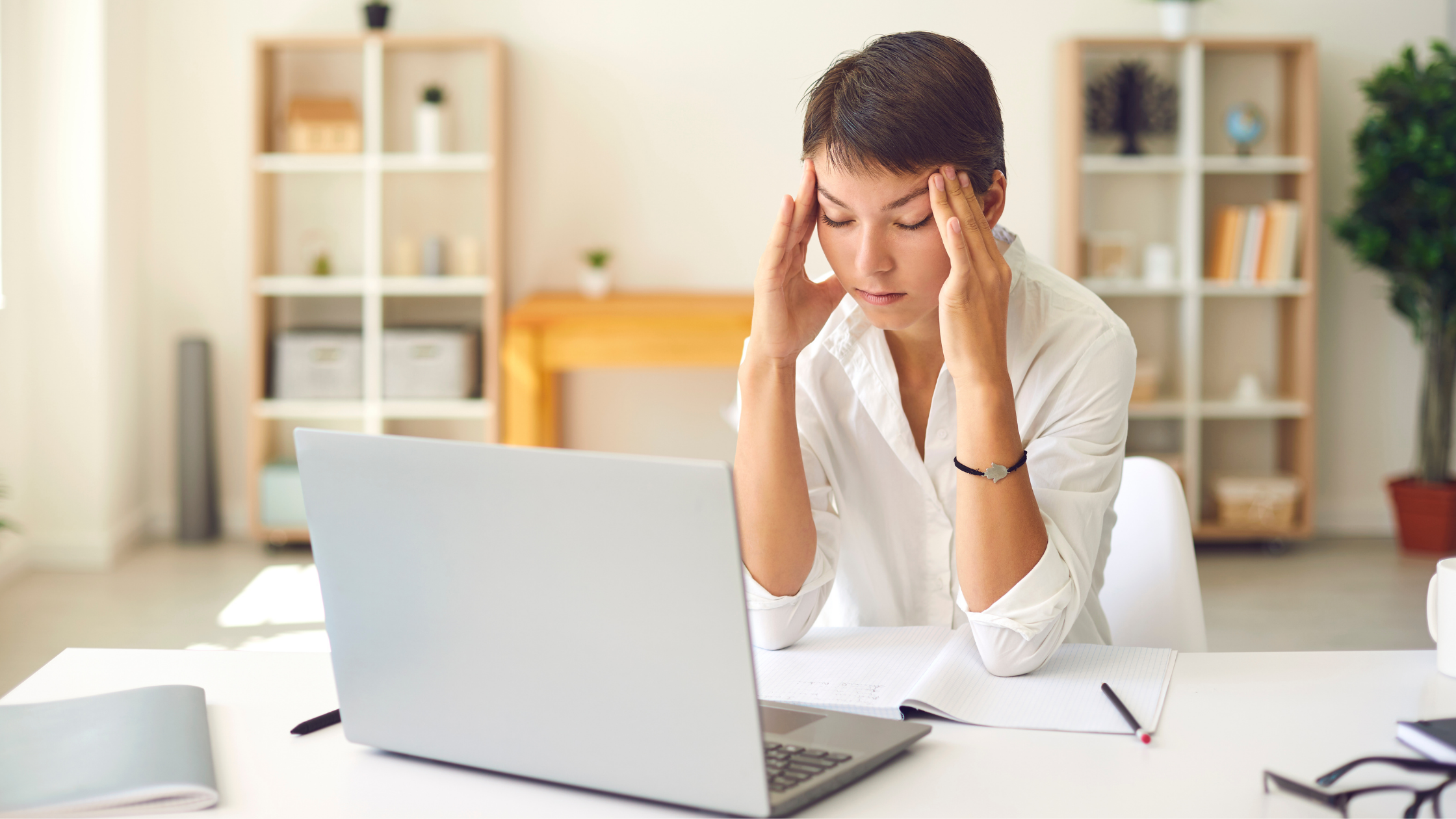
In this article, I want to discuss the subject of concussions caused by car accidents and the importance of getting appropriate examinations to diagnose and treat concussions where they exist. According to the Cleveland Clinic:
“A concussion is a mild traumatic brain injury that results from a bump, violent jolt or blow to your head that disrupts normal brain function. A concussion can also be caused by a hit to your body that is strong enough to cause your head to forcefully jerk backwards, forwards or to the side.”
Concussions can occur as a result of a hit to the head or the body. While not all car accidents result in concussions, if you suspect or have experienced any symptoms of a concussion, it is critical that you receive appropriate examination.
If you have been in a car accident and have any of these symptoms, ask your doctor to administer the necessary tests to check for concussion or to refer you to a neurologist or specialist.
- Headache
- Blurred or double vision
- Dizziness, balance problems, or trouble walking
- Confusion and saying things that don’t make sense
- Being slow to answer questions
- Slurred speech
- Nausea or vomiting
- Not remembering what happened
- Not feeling well
It is important to know that symptoms of a concussion usually happen right away, but can show up hours or days after an injury.
What Happens In a Concussion?
What exactly happens in a concussion? Your head and spine are designed to protect your brain from injury. If you receive a hit to the head or the body, the blow you receive can jolt to the head, can hurt the brain directly, or make the brain move around and bang up against the hard bone of the skull. This changes the signals between nerves, which causes concussion symptoms.
How Are Concussions Diagnosed?
To diagnose a concussion, your doctor may ask about:
- How and when the head or body injury happened
- What symptoms you are experiencing
- Test memory and concentration
- Do a physical exam and test balance, coordination, and reflexes
If you feel you have a concussion or are showing symptoms of a concussion it is important that you insist on getting this fully examined.
At Horn Law, we have helped many patients receive appropriate testing, treatment, and compensation for concussions caused by car accidents.
Treating a Concussion
While physical therapy and some medications can be prescribed to help concussion symptoms, rest is one of the most important treatments for a concussion because it helps the brain to heal. Rest nearly completely for the first few days after a head injury, then slowly begin to “exercise your brain.” The unused, “stagnant” brain remains stagnant if not used and lengthens recovery. *
About Doug Horn
Douglas R. Horn is the Lead Attorney of The Horn Law Firm, P.C. where he exclusively represents persons who are injured in accidents, including cases arising from motor vehicle collisions, work & industrial accidents, and dangerous conditions.
Since 1991, Horn has compiled a track record of success in obtaining maximum recovery for his clients, concentrating in cases involving neck, back, and spinal injuries, head/brain trauma, fractures, injuries requiring extended medical care, and catastrophic injury.
As Horn’s law practice has increasingly focused on motor vehicle accident law and crash litigation, he also dedicates a significant amount of his work to the advancement of driver safety, particularly in the area of teen driver protection.
In addition to his law practice, Horn frequently presents on personal injury law to national attorney audiences, including strategies to maximize legal recovery for traumatic brain injury, neck, back, and spinal injury, orthopedic injury, and complex/catastrophic injury.